TL;DR: A good continuous development workflow makes developers more productive by providing constant feedback during the build, deploy, and test cycle. These 5 services will complete your CI pipeline.
Continuous development
Continuous development is a process software development teams use to increase developer productivity, build and deploy code more frequently, and continuously test an application to get immediate feedback on new releases.
A complete CI pipeline is made up of three major parts:
- Integration: Build code and run unit tests
- Delivery: Deploy your application
to a
stagingorproductionenvironment. - Testing: Run automated QA tests to validate new releases and deployments.
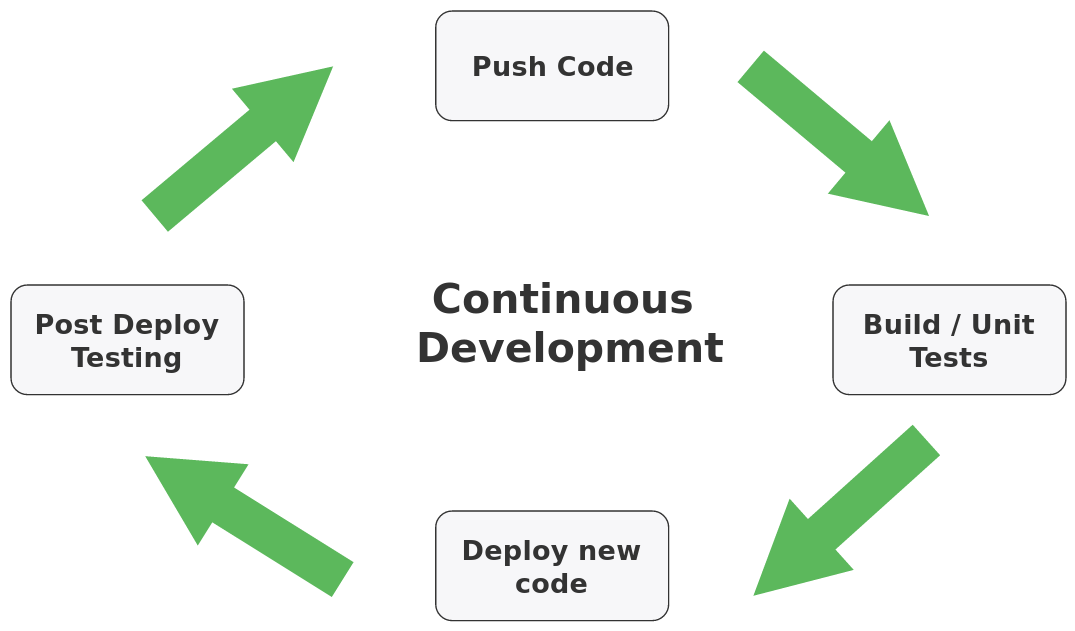
This post will discuss each phase of continuous development workflow and provide some tools and examples for each step. Most services mentioned below are hosted servces with free plans, particularly ones that integrate with a GitHub deployment pipeline.
Continuous integration
Continuous integration is
a process for frequently building and testing new code
changes. Generally, code is hosted on a central repository, like
Git, that is monitoring by a CI service. When changes are detected,
the CI service will pull and build the new code.
Most CI services allow you to have a configuration file checked into
your repository (eg, a .travis.yml) that describes how to build your
application and run the test suite. A good CI service provides several
benefits:
- Ensures that code can be built and executed
- Requires that all unit tests are passing
- Immediately alerts developers of build failures.
Tools
There are many great hosted CI services that work with your existing GitHub repositories. It's worth trying a few to see what works best for your project. Two of the most widely used CI services are:
Circle CI 
_Free and paid plans available._ [Website](https://circleci.com)
The modern continuous integration and delivery platform that software teams love to use. - CircleCI
Travis CI 
_Free and paid plans available._ [Website](https://travis-ci.org)
Easily sync your GitHub projects with Travis CI and you’ll be testing your code in minutes! - Travis-CI
Continuous delivery
Continuous delivery is
the process of deploying new versions of an application
frequently, sometimes several times daily, to testing, staging,
and production environments. An important part of continuous
delivery is that it makes application changes more reliable by by
providing a consistent, reproducable pipeline for pushing new
features to your users.
Deploying an application to a staging or production environment
can get hairy, but a good delivery system will provide you with the
tools and automation to make it simple. Being confident about
rapidly pushing code and having a good deployment process can
greatly improve a product.
Tools
Like CI tools, there are a lot different services for setting up continuous delivery. One of the most powerful and widely used is Heroku Flow.
Heroku Flow 
_Free and paid plans available._ [Website](https://www.heroku.com)
Heroku Flow brings together Heroku Pipelines, Review Apps and GitHub Integration into an easy to use structured workflow for continuous delivery, so you can test early and deploy often, with better results for your users. - Heroku
If your team is already using GitHub to host code,
the
Heroku GitHub integration provides
a way to automatically deploy every pull request to a staging
environment
via
Review Apps.
Continuous testing
The final step in a solid continuous development pipeline is automated testing and QA. Continuous testing is the process of running automated integration tests against new deployments. This gives teams and developers a way to immediately test and validate every deployment.
Take the Heroku Review App example -- when a pull request is opened on your repo, and the code is deployed to a review environment, and your automated QA tests are run against the live application to ensure the web service is working as expected.
When your application is deployed to a production environment, these
same tests are run against the new release. Although a dedicated
staging or testing environment is not required, it does provide
huge benefits to teams who have many developers pushing to the same
repo. In either case, a good continuous testing service will allow
you to run post-deploy smoke tests immediately after every
deployment.
Tools
Tools for continuous testing can range from manual QA teams and custom scripts for monitoring and testing API endpoints. Assertible is one hosted service that let's you create a post-deployment testing pipeline.
Assertible 
_Free and paid plans available._ [Sign up for a free account](/signup)
Reduce bugs in web applications by using Assertible to create an automated QA pipeline that helps you catch failures & ship code faster. - Assertible
You are on the Assertible Blog so I might be a bit biased. Post deployment testing is, however, a crucial part of a good continuous development workflow that will enable you and your team to write better code and gain confidence in your release cycle.
Wrapping up
What tools does your continuous development pipeline consist of? Shoot us a message on Twitter and let us know!
The assertible/deployments contains more information on integrating continuous testing into your existing workflow. Check it out and sign up for a free Assertible account to start testing your deployments!
:: Cody Reichert
Cofounder @ Assertible
Categories
The easiest way to test and
monitor your web services
Reduce bugs in web applications by using Assertible to create an automated QA pipeline that helps you catch failures & ship code faster.
Recent posts
Tips for importing and testing your API spec with Assertible 05/26/2020
New feature: Encrypted variables 10/30/2019
New feature: Smarter notifications 5/17/2019