At Assertible, we automatically run tests against our APIs after every deployment to reduce bugs, validate functionality, and save developer time.
Having a reliable process in place for testing and validating API deployments provides a huge amount of confidence when deploying new changes into production. Running automated test-suites immediately after a deployment is the best way to augment your continuous integration pipeline to be certain that your application is ready for users. It also saves developers time by decreasing the need for manual testing.
At Assertible, we have integrated continuous web service testing as a first-class step in our continuous integration & delivery pipeline.
In this post I'll discuss our continuous integration pipeline and how we validate releases by testing our web services in several stages before it's shipped to production.
How we continuously test our web services
At Assertible, our continuous integration, delivery, and testing setup is simple:
- Push code to repos hosted on GitHub.
- Run unit tests on Circle CI.
- Build deliverables on Circle CI.
- Deploy the new app to staging or production on Elastic Beanstalk.
- Execute automated API tests on the new app with Assertible.
Running API tests automatically after every deployment quickly validates and provides feedback about the release.
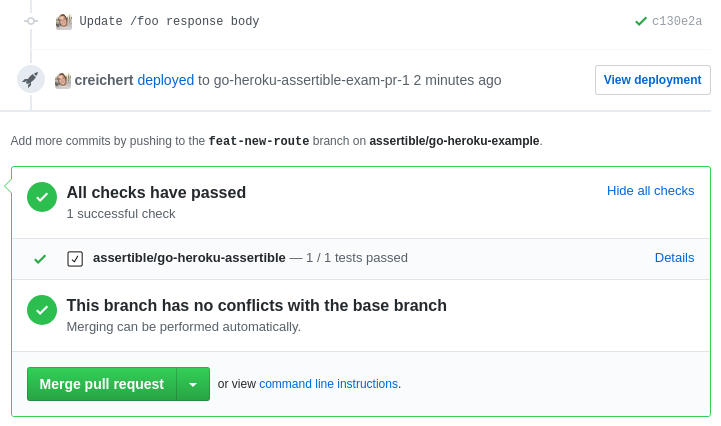
For example, when a pull request is opened, code is built and deployed to a staging environment. API tests are automatically run against the new app on the staging environment.
If the Assertible tests do not pass when run against the new deployment, the GitHub status check on the pull request will fail and tell us the code shouldn't be merged.

One of the most important aspects of automated QA tests is to keep it simple. Not only can too many end-to-end tests become flaky, they take a long time to run and can be difficult to debug. For this reason, we have an abundance of smaller integration tests which validate a unique aspect of our API or web service.
We've discussed techniques for improving automated QA pipelines in detail in our techniques to reduce api testing errors and improve your QA process.
More on the Assertible GitHub integration
By using Github we're able to take advantage of the Assertible GitHub deployment integration and deployment events.
After the code is built and in the process of being deployed to a staging server, Assertible receives deployment status events from GitHub via webhooks. When a deployment is successful, Assertible runs all tests for that API and updates the status check on a pull request.
The [assertible/deployments](https://github.com/assertible/deployments)
repo has instructions on setting up GitHub deployments as a part of
your CI with a simple script.
If you are not using GitHub, it's probably easiest to use
the [deployments API](/docs/guide/deployments)
Another neat part of using GitHub status checks with Assertible is
that we can see the result of our API tests on the master branch.
Any commit made to the master branch means a deployment to
production. By looking in the commit history we can see that the API
tests were all successful.

API testing with Assertible
Our API test cases live in Assertible. Tests are configured to:
- validate all API endpoints
- test core functionality
- make assertions on response data integrity like link checking, JSON Schema validation, and JSON path data
The image below demonstrates some of the tests that are run when a new version of the API is deployed.

Before we had a robust continuous testing pipeline in place, tests had to be triggered manually or executed directly from random scripts in our continuous integration pipeline.
Both approaches are time-consuming and error prone. Of course, in-house software can be written to make testing easier and that's what many teams do. However, in-house solutions require developer time, organization, and in many cases a team large enough to justify a dedicated QA developer -- we believe there is a better way to test web services.
Because tests are executed as a first-class step in our continuous integration pipeline, alerts are propogated directly to the source of the code changes, pull requests. If a test fails, the status check on GitHub will have a link directly back to the failing test result to easily see why:

Uh oh! It looks like we broke some authentication logic in the
/tests handler. This is where continuous testing saves our skin and
our time (and in some cases our job!).
This is why we test every. single. deployment automatically. When all tests are passing, we can happily merge knowing that the release has been validated and tested. Further, production deployments will be tested as well.
With a solid continuous testing automation workflow in place, manually testing endpoints is unnecessary. Furthermore, with opportunistic automation (on deployments and scheduled intervals), we've reduced the need to setup and maintain in-house tests scripts.
Start testing your web services now!
Assertible is free to use. Contact us if you have any questions or
feedback!
Continue the discussion
I always enjoy hearing how other teams test and validate API deployments. Tweet at me (@CodyReichert) or us (@AssertibleApp) and let's see what you're working with!
Assuredly yours,
Cody Reichert
Categories
The easiest way to test and
monitor your web services
Reduce bugs in web applications by using Assertible to create an automated QA pipeline that helps you catch failures & ship code faster.
Recent posts
Tips for importing and testing your API spec with Assertible 05/26/2020
New feature: Encrypted variables 10/30/2019
New feature: Smarter notifications 5/17/2019