The ideal time to automatically run API and web app tests is immediately after a deployment. Using the Assertible deployments API, you can run tests for a web service as part of your continuous-integration or delivery pipeline and track deployments to specific versions of your application.
If the code for your web service is hosted on GitHub, you can also create status checks and deployment events for commits and pull requests.
Check out our GitHub integration![]()

The easiest way to create a deployment is to run a simple curl
command from your continuous integration pipeline or deployment
process:
curl -u $ASSERTIBLE_API_TOKEN: -XPOST https://assertible.com/deployments -d'{
"service" : "'"${ASSERTIBLE_SERVICE_ID}"'",
"environment" : "production",
"version" : "v1"
}'
See the examples for more examples.
GitHub
When you post a deployment to Assertible, it's possible to propogate
the test statuses and deployment details to GitHub pull requests (and
other refs & branches like master).
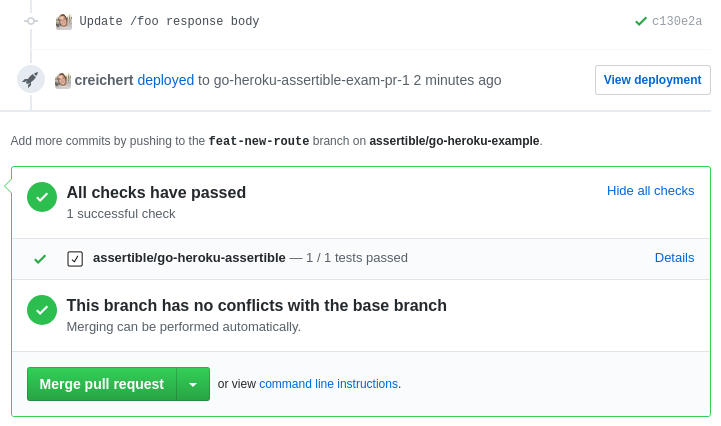
For example, in the picture above, a deployment is created on
assertible-staging with a direct link to the staging environment URL
using the View deployment button, as well as the status of tests
directly in the pull request checks under CircleCI.
Connect your web service to GitHub:
All you need to do to start creating GitHub deployments and status
checks is to connect your web service to GitHub and use the github:
true parameter in the call to POST /deployments.
When the github: true parameter is used, Assertible posts deployment statuses
and test results to the GitHub API for the ref you provide in the deployment
script after executing your tests. The ref must be the full SHA1 hash of the
commit (don't use the short hash).
Continuous integration services usually populate the environment with a variable
containing the commit. For example, CircleCI uses CIRCLE_SHA1. We recommend
using the equivalent of $ git rev-parse HEAD.
POST a deployment to Assertible. Heroku
will create deployment events for the deployments and Assertible will
recieve the events and run your tests. Your web service only needs to
be connected to the correct repository.
External GitHub deployment integrations
If you are deploying code using a continuous delivery service like Heroku Pipelines or Heroku Review Apps, deployment events are already posted to the repository for you automatically. See our blog Automate smoke tests for a Go API on Heroku for a more detailed example.
Deployments API examples
Successful request
If the request succeeds, it will respond with the unique id of the
deployment:
curl -XPOST -u $ASSERTIBLE_API_TOKEN: https://assertible.com/deployments -d'{
"service" : "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440000",
"environment" : "production",
"version" : "v1.2"
}'
{
"id":"caacafdc-8ddc-4245-a0f4-f6715c5d9478",
"runId": "abcd1234",
"testRun": {
"status": "TestRunPending"
}
}Failed request
If creating the deployment fails, an error will be returned:
curl -XPOST -u $ASSERTIBLE_API_TOKEN: https://assertible.com/deployments -d'{
"service" : "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440000",
"environment" : "staging",
"version" : "v1.2"
}'
{"code":"InvalidRequestError","message":"Cannot parse request body\n\"Error in $: key \\\"service\\\" not present\"\n"}GitHub deployment
If the request succeeds, it will respond with an empty JSON object:
SHA=$(git rev-parse HEAD)
curl -XPOST -u $ASSERTIBLE_API_TOKEN: https://assertible.com/deployments -d'{
"service" : "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440000",
"environment" : "production",
"version" : "v1",
"ref" : "'"${SHA}"'",
"github" : true
}'
{
"id": ...,
"runId": null,
"testRun": null
}Parameters
These parameters can be used in a request to POST /deployments:
| Name | Type/Required | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
service |
UUID required |
The web service/API id. This can be found in the Assertible dashboard under the Deployments tab (look for Bash / Command-line). |
n/a |
version |
String required |
A unique textual representation of the application version. For example v1.0 or even a commit reference like cc0ab3f. |
n/a |
environment |
String optional |
Run tests using a named environment. The environment must match a valid environment name for the target web service, unless environmentUrl is also specified. See our environments documentation for more information. |
production |
environmentUrl |
String optional |
Run tests against a specific url, known as a transient environment. See our environments documentation for more information. | n/a |
ref |
String optional |
A unique source control reference or commit hash. For version control systems like Git, we recommend using the full commit reference hash. This parameter is required when using the github parameter. Ensure this variable contains the full SHA1 of the commit that is deployed, not just a prefix.Continuous integration services usually populate the environment with a variable containing the commit. For example, CircleCI uses CIRCLE_SHA1. We recommend using $ git rev-parse HEAD to generate the commit hash. |
n/a |
url |
String optional |
An external url for viewing further details about the deployment. | n/a |
github |
Boolean optional |
If the github parameter is true, Assertible will create deployment events and corresponding status checks for the specified repository and ref on GitHub.You can visualize the results of test runs on your team's Pull Requests and commit history. See the GitHub docs for more details. Your web service must be connected to a GitHub repository to use this parameter. |
n/a |
repository |
String optional |
If your web service has multiple GitHub integrations to separate repositories, use this parameter to specify the repo being deployed to avoid executing redundant tests. The github parameter must be true to use repository. See the GitHub docs for more details.Your web service must be connected to a GitHub repository to use this parameter. |
n/a |
tests |
Array<UUID> optional |
Restrict the test run to a given list of test ids, e.g. "tests" : ["be6df68d-e32f-47c5-bf6f-b1c208182b6f", "f0ca8862-3d29-4b57-910f-efa222dd9aa0"].To access a test's id, navigate to a test and find the trigger URL under the Settings tab. |
n/a |
testGroups |
Array<string> optional |
Restrict the test run to a given list of test groups, e.g. "testGroups" : ["deployment-group", "health-check"].This option is not mutually exclusive with the tests parameter. Both parameters can be used at the same time or separately to have complete control over what tests are executed. |
n/a |
wait |
Boolean optional |
Wait for all tests in the run to complete before sending the API response, including the final status. | false |
POST request is made twice, the deployment is
updated. This only has an impact for
optional parameters
like ref or url. A unique deployment is
represented by the service, environment name, and version combination.
The easiest way to test and
monitor your web services
Reduce bugs in web applications by using Assertible to create an automated QA pipeline that helps you catch failures & ship code faster.