Syncing makes it easy to keep your Assertible tests up-to-date with the latest changes in OpenAPI, Swagger, and Postman API specification documents.
For teams that maintain API definitions in OpenAPI, Swagger, or Postman collection format, a pain-point is often keeping tests up-to-date with the latest changes in the spec. To solve this problem, we've implemented sync.
Learn more below about how it works and getting started:
- Syncing a specification
- How sync identifies unique operations
- Parameter and header default values
- Syncing OpenAPI or Swagger definitions
- Syncing Postman collections

Syncing a specification
Tests can be synced in two ways:
- Importing new tests from an OpenAPI, Swagger or Postman collection.
- Re-importing an existing OpenAPI, Swagger, or Postman import from a URL.
Syncing tests from a new import
When you import new tests on an existing web service, Assertible will look for any previous imports from the same specification. This is useful if you are importing your spec from a file or want to sync only certain tests:

Syncing tests from an existing import
When you import a specification from a URL, Assertible saves that information so you can easily sync with the specification hosted on that URL at the click of a button or using a simple API call.
A list of these available imports can be found on the Imports tab of your web service's Settings page:
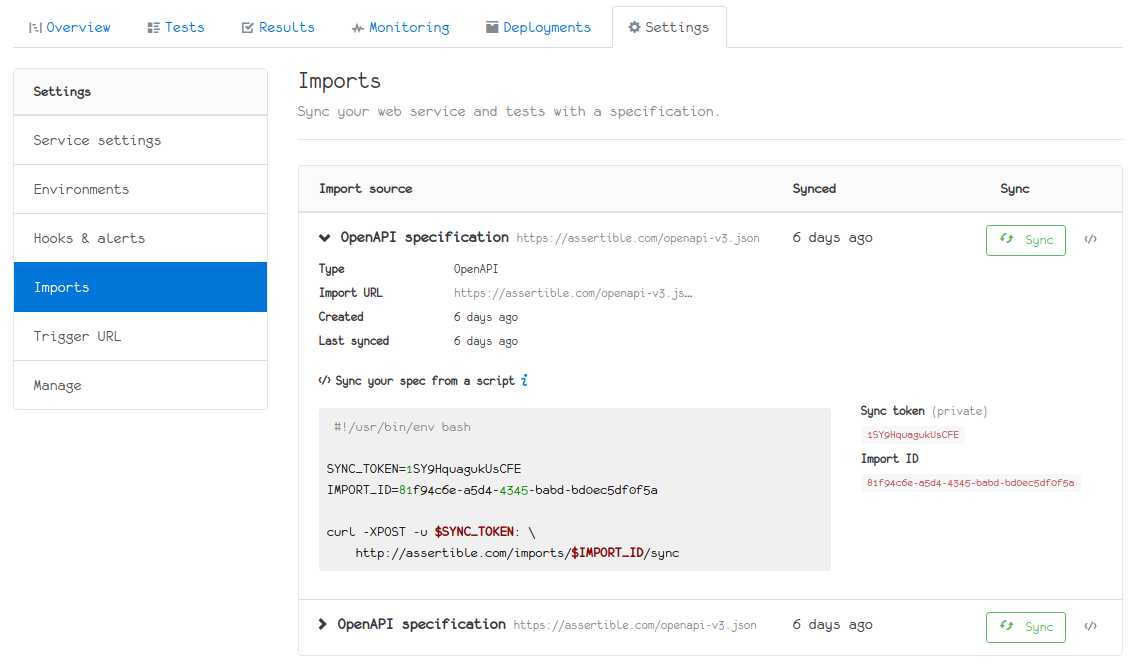
Sync API
When sync'ing tests from the command-line or a CI job, the following parameters are supported:
| Name | Type/Required | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
tests |
Array<UUID> optional |
Restrict the sync to a given list of test ids, e.g. "tests" : ["be6df68d-e32f-47c5-bf6f-b1c208182b6f", "f0ca8862-3d29-4b57-910f-efa222dd9aa0"].To access a test's id, navigate to a test and find the trigger URL under the Settings tab. |
n/a |
Sync API examples
Sync a subset of tests
curl -XPOST -u $ASSERTIBLE_SYNC_TOKEN: https://assertible.com/imports/$IMPORT_ID/sync -d'{
"tests": ["123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426655440000"]
}'If the request succeeds, it will respond with the number of tests imported or synced.
How sync identifies unique operations
It's important to understand how Assertible uses the information in your import source to identify and import unique tests so that you can use the full power of sync to your advantage.
Assertible iterates through each unique definition (Operation for
OpenAPI/Swagger and Item for Postman Collections) in your spec and creates or
updates tests based on two distinct processes:
Identify a unique determinstic key for the test
For OpenAPI/Swagger definitions, each unique
METHOD/ENDPOINTcombination (orOperation) is defined as a unique Assertible test. This behavior can be overriden usingoperationId. See the section below on syncing OpenAPI/Swagger documents for more details.For Postman Collection definitions, each unique collection
Itemis defined as a unique Assertible test. This behavior can be overriden usingItem'sidparameter. See the section below on syncing Postman collections for more details.Map data and populate your Assertible test from your unique spec item
Assertible uses as much information as possible to intuitively use the information from your spec to configure as much test and assertion data as possible. Unintrusive defaults that are the most likely to result in a successful test run with the least necessary configuration are used when possible.
See the respective sections for OpenAPI, Swagger, and Postman below for a comprehensive guide on what fields in a spec map to Assertible test configuration values.
Parameter and header default values
Assertible uses some simple conventions to determine which parameter values are used for testing.
In particular, sync looks at the values in the example, enable/disable,
default, and required fields, then creates tests using the rules described
below to determine which value to assign to each parameter.
The example parameter overrides default
By convention, sync prefers the value for the example parameter to the value
for the default parameter. The default value is used only when no
example value is specified.
Enabled/disabled parameters
Also by design, the sync process preserves the enabled/disabled status of parameters and headers across successive sync operations. So from the Test page, you can manually enable/disable any parameter(s), and be confident that all subsequent sync or import actions will preserve those settings automatically.
Optional parameters
Assertible will import optional parameters (those tagged with required: false)
when there is a default value specified, but they'll be disabled for test
purposes. Those parameters will be shown as "undefined" on the Test page.
No validation of data types
It's also important to remember that sync does not validate the data type of any parameter. That means the sync process will create tests according to the preferences described above whether the selected values match the specified data type or not. While that helps avoid tedious interruptions to the sync process, it doesn't prevent test failures due to type mismatch errors. If a test fails, be sure to check for data type mismatches as part of initial troubleshooting.
Syncing OpenAPI or Swagger definitions
By default, when you import an OpenAPI or Swagger definition Assertible creates
a test for each unique
Operation. In practice,
this is determined using the ENDPOINT/METHOD as the key for each test.
In practice, this means that if you change the operation's method from GET
to PUT in your spec, Assertible will create a new test and sync that for all
future imports.
operationId field on your item will
override Assertible's default unique test identification, giving you
complete control over all future updates to a specific test.
OpenAPI import fields
See the legend below for references to OpenAPI documentation
| Assertible field | OpenAPI field | Default |
|---|---|---|
| endpoint | The key of the Paths entry [0] |
n/a |
| method | The key of the Path Item key [1] |
n/a |
| name | The summary value for the Operation [2] |
Combination of operation and path name |
| description | The description value for the Operation [2] |
null |
| variables | For each Parameter[3] in the Operation entry where in=path, a test variable is defined. |
[] |
| query parameters | For each Parameter[3] in the Operation entry where in=query, a test query paramer is defined. |
[] |
| headers | For each Parameter[3] in the Operation entry where in=header, a test header is defined. If any requestBody[4] body is also imported, an additional header is defined for the corresponding Content-Type |
[] |
| auth | Auth is imported to your web service's environment based on the SecurityRequirement defined in the spec |
Uses default auth if no other options are available |
| request body | The requestBody body for an Operation [4]. An additional header is imported for the corresponding Content-Type. |
[] |
| status code assertion | Imported from responses in the Operation. The lowest status code possible is used with the exception that 2XX is preferred over 1XX. |
200 |
| json schema assertion | Imported from responses in the Operation. If any response defines a schema, that response is preferred. If a JSON Schema assertion is defined for a response then the status code assertion will contain the correct code. To override this behavior for successful requests, simply define a responses entry with a 200 or desired status code. |
[] |
- [0]openapi
pathsobject - [1]openapi
path itemobject - [2]openapi
operationobject - [3]openapi
parameterobject - [4]openapi
requestbodyobject - [5]openapi
security requirementobject
See our blog post Sync changes from OpenAPI/Swagger specifications with Assertible API tests for more details on how this feature works.
Syncing Postman Collections
By default, when you import a Postman Collection Assertible creates a test for
each unique
collection item.
However, Assertible still ensures unique tests by using a combination of the
METHOD/ENDPOINT to reliably sync future changes.
id field on your item to override
Assertible's default unique test identification to have complete
control over all future updates to a specific test.
Postman Collection import fields
See the Postman Collection Schema docs for clarification on references the references in the table below.
| Assertible field | Postman Collection field | Default |
|---|---|---|
| method | The method defined in the Item request configuration. |
GET (used when the request is a plain URL) |
| endpoint | The path portion of the request url. | / |
| name | The item name. |
Combination of operation and path name |
| description | The item description or parent Collection description. |
null |
| variables | All variables defined in the item are imported as test variables. |
[] |
| query parameters | Extracted from the request url. | [] |
| headers | All item headers are imported as test headers. |
[] |
| request body | The item body. |
null |
| status code assertion | Status code 200 is used on all tests. |
200 |
The easiest way to test and
monitor your web services
Reduce bugs in web applications by using Assertible to create an automated QA pipeline that helps you catch failures & ship code faster.